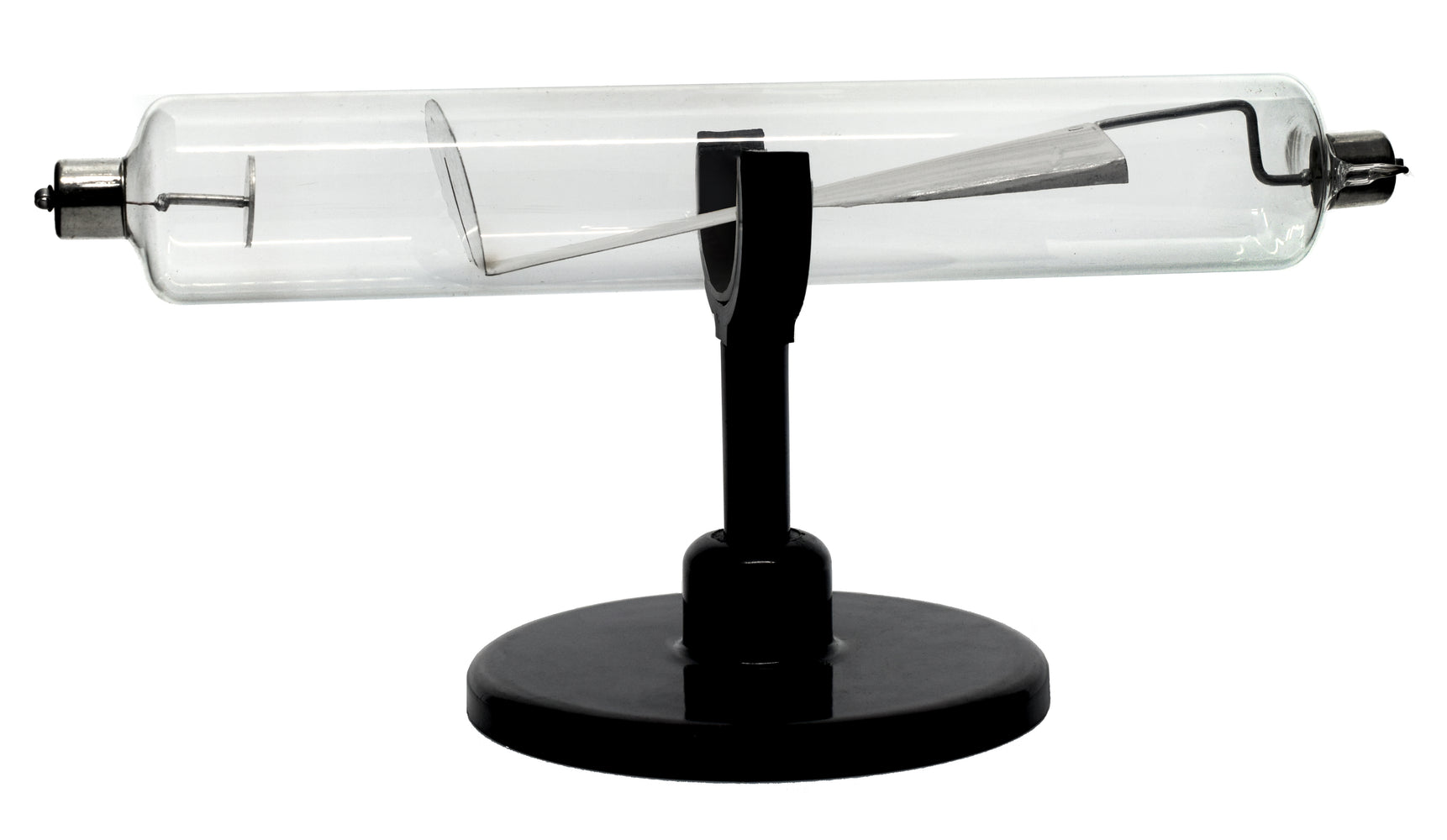



Helmholtz coil, a device for producing a region of nearly uniform magnetic field, is also used to apply a quantifiable magnetic field by passing a current through them.Ī magnetic field will cause a force to act on the electrons which are perpendicular to both the magnetic field and their direction of travel. This enables us to see the path of the beam. These accelerated electrons collide into the gas inside the tube, thereby allowing it to glow. The cathode ray tube (CRT) is a vacuum tube, in which electrons are discharged from the cathode and accelerated through a voltage, and thereby gains acceleration of some 600 km/s for every volt. The derivation of the formula used to calculate the charge to the mass ratio:įor Electric Field the force on a particle isįor Magnetic Field the force on a particle moving with velocity is:įrom Newton’s law Of motion, vertical displacement is: From this experiment, he concluded that the electrostatic deflection is the same as the electromagnetic deflection for the cathode rays and he was able to calculate the charge to mass ratio of the electron.Īfter these three experiments, he deduced that inside the atom there consist of a subatomic particle, originally named ‘corpuscle’, then changed to ‘electron’ which is 1800 times lighter than the mass of hydrogen atom (Lightest atom). Now he changed the direction of the external magnetic field and found that the beam of electrons is deflected in the opposite direction. The cathode ray is deflected by the magnetic field. Now he applied a magnetic field across the cathode ray tube by using an external magnetic field. Firstly, he applied an electric field in the path between anode and cathode and measured the deflections from the straight path. He had already deduced that the particles were negatively charged. For the experiment, he used the cathode ray tube and with a high applied potential difference between the two electrodes, with the negatively charged cathode producing the cathode rays. Then he performed the third experiment, to know the nature of the particles and reduce the mass of the particles as they had too small of a mass to be calculated directly. This proved that the cathode rays were negatively charged. When the charged metal plates were introduced he found that the cathode rays bent away from the negative plate and towards the positive plate. Instead of an electrometer at one end of the Cathode Ray Tube, he used a fluorescent coated tube that would glow where the cathode ray hit it. Now, he put a negatively charged metal plate on one side of the cathode rays to go past the anode, and a positively charged metal plate on the other side. Then he conducted a Second experiment, to prove the charge carried by the cathode rays was negative or positive. From this, he deduced that the electric charge and the cathode rays must be combined and are the same entity. From the first experiment, he discovered that the electrometers stopped measuring electric charge. The metal had two small diversions(slits), leading to an electrometer that could measure a small electric charge. He built his cathode ray tube with a metal cylinder on the other end.
Thompson, conducted his first cathode ray tube experiment to prove that rays emitted from an electron gun are inseparable from the latent charge. Screen: - The inner layer of the screen is coated with phosphorus, and produces fluorescence when cathode rays hit the screen by a process of phosphorus excitation.Īquadag: - It is an aqueous solution of graphite used to collect the secondary emitted electrons which are required to keep the cathode ray in electrical equilibrium. The electron gun has a heater, cathode, pre-accelerating anode, focusing anode and accelerating anode.ĭeflecting Plates: - They produce a uniform electrostatic field only in one direction, and accelerate particles in only one direction. A wire is connected from anode to cathode to complete the electrical circuit.Įlectron Gun Assembly: - It is the source of the electron beams. When a potential difference is applied, the electrons jump to an excited state and travel at high speeds to jump back-and-forth inside the vacuum glass chamber and when some cathode rays certain molecules of the cathode screen, they emit light energy. Since electrons are repelled by the negative electrode, the cathode is the source of cathode rays inside a vacuum environment. The cathode is a negative electrode, Anode is the positive electrode. Cathode rays are a beam of negatively charged electrons traveling from the negative end of an electrode to the positive end within a vacuum, across a potential difference between the electrodes.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
